FLV 格式:为什么直播首选这个流媒体格式?
介绍 FLV 封装格式概览、Audio Tags 解析、Video Tags 解析、Data Tags 解析等基础知识。
想要学习和提升音视频技术的朋友,快来加入我们的【音视频技术社群】,加入后你就能:
- 1)下载 30+ 个开箱即用的「音视频及渲染 Demo 源代码」
- 2)下载包含 500+ 知识条目的完整版「音视频知识图谱」
- 3)下载包含 200+ 题目的完整版「音视频面试题集锦」
- 4)技术和职业发展咨询 100% 得到回答
- 5)获得简历优化建议和大厂内推
现在加入,送你一张 20 元优惠券:点击领取优惠券
(本文基本逻辑:FLV 封装格式概览 → Audio Tags 解析 → Video Tags 解析 → Data Tags 解析)
FLV(Flash Video)是 Adobe 公司推出的一种流媒体格式,它的特点是封装后的音视频文件较小、封装规范简单,因此适合在互联网上进行传输和使用。在浏览器普遍支持 Flash 插件的时代,FLV 格式的视频非常流行。但是随着主流的浏览器平台逐步放弃了对 Flash 插件的支持后,以及移动互联网的兴起,App 取代浏览器成为更多内容的载体,在短视频领域 FLV 的地位逐步被 MP4 取代。但是,在直播领域,由于 RTMP 推流、HTTP-FLV 播放的整套方案低延时的特性,以及服务端普遍提供 HTTP Web 服务,能更广泛的兼容 HTTP-FLV,使得 FLV 仍然是大多数直播产品的首选流媒体格式。
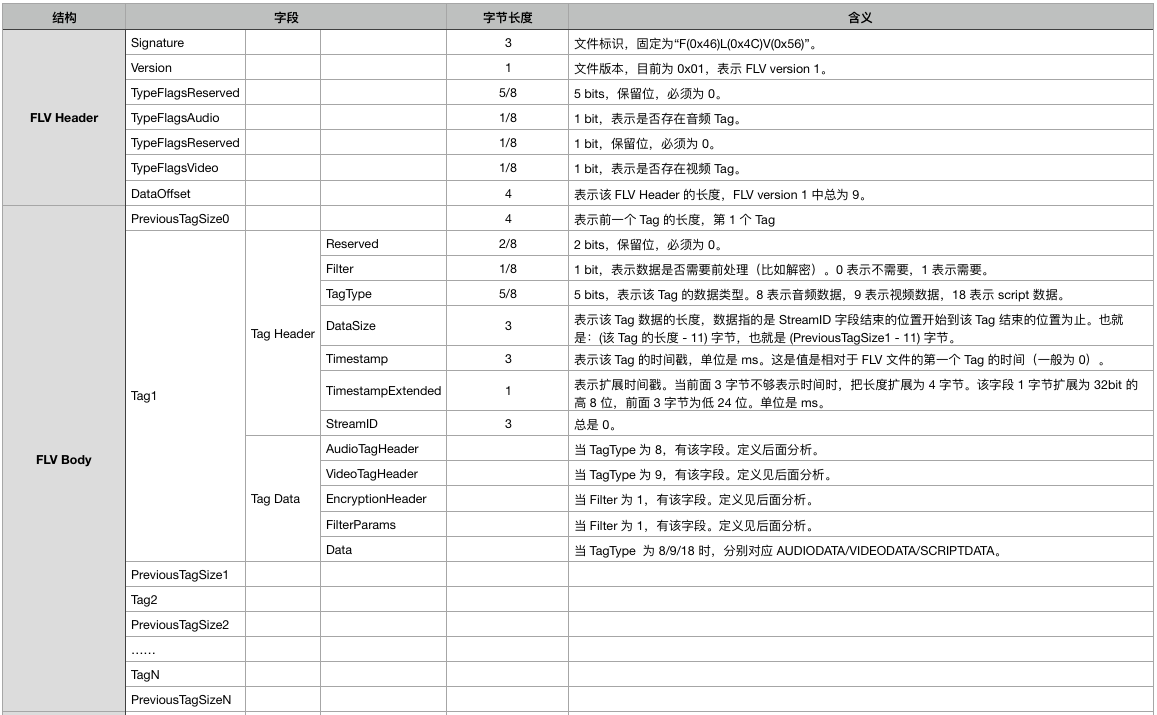
1、FLV 格式概览
FLV 文件由一个 FLV Header 和一个 FLV Body 组成,在 FLV Body 中则由多组 (PreviousTagSize + Tag) 组成。
FLV 中 Tag 的类型有三种:
- Audio Tags
- Video Tags
- Data Tags
Tag 中包含着 audio、video、scripts 的元信息,加密信息(可选)以及对应的实际数据。
总体来讲,FLV 的结构大致如下表所示:
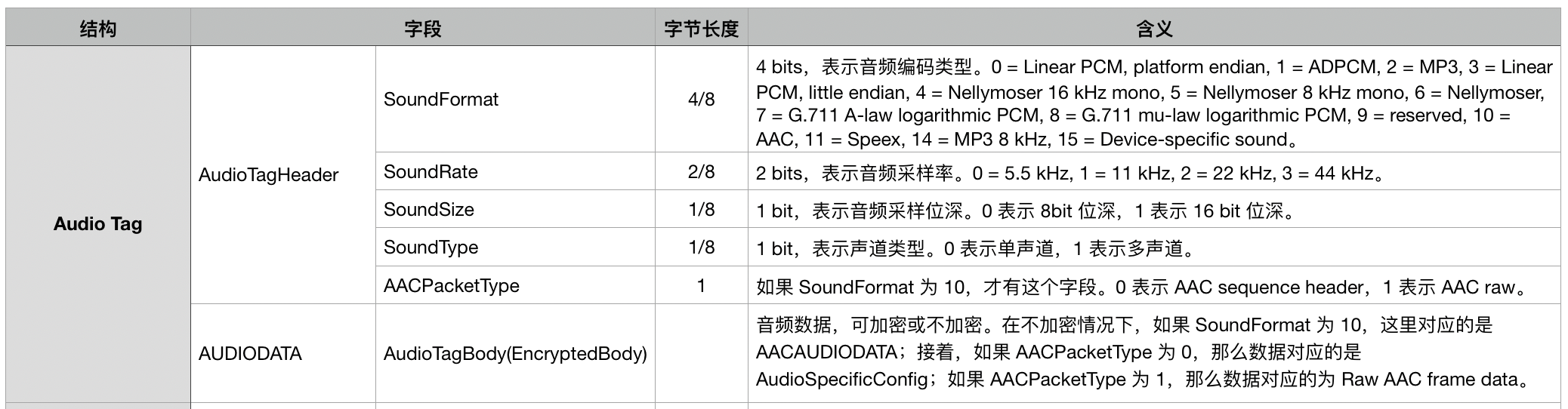
2、Audio Tags 解析
Audio Tag 的结构大致如下所示:
通常在 AudioTagHeader 后面跟着就是 AUDIODATA 数据了,但是对于 AAC 格式的音频数据来说,AudioTagHeader 会多一个字段 AACPacketType 来表示 AACAUDIODATA 的类型:如果 AACPacketType 为 0,那么数据对应的是 AudioSpecificConfig;如果 AACPacketType 为 1,那么数据对应的为 Raw AAC frame data。
为什么 AudioTagHeader 中已经有了音频的相关参数,还需要在这里来一个 AudioSpecificConfig 呢?这是因为当 SoundFormat 是 AAC 时,SoundType 需要设置为 1(立体声),SoundRate 需要设置为 4(44k Hz),但这并不说明文件中 AAC 编码的音频必须是 44k Hz 的立体声。播放器在处理 AAC 音频时,需要忽略 AudioTagHeader 中的音频参数,而使用 AudioSpecificConfig 的参数来初始化解码器。
在 FLV 的文件中,一般情况下 AudioSpecificConfig 只会出现一次,即第一个 Audio Tag。如果音频使用 AAC,那么这个 Tag 就是 AAC sequence header,即 AAC 音频同步包。AudioSpecificConfig 的结构在 ISO/IEC-14496-3 Audio 标准中有做说明。
下面是 ISO/IEC 14496-3, 1.6.2.1 AudioSpecificConfig:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
AudioSpecificConfig() {
audioObjectType = GetAudioObjectType();
samplingFrequencyIndex; // 4 bslbf
if (samplingFrequencyIndex == 0xf) {
samplingFrequency; // 24 uimsbf
}
channelConfiguration; // 4 bslbf
sbrPresentFlag = -1;
psPresentFlag = -1;
if (audioObjectType == 5 || audioObjectType == 29) {
// ...
}
else {
extensionAudioObjectType = 0;
}
switch (audioObjectType) {
case 1: case 2: case 3: case 4: //...
GASpecificConfig();
break:
case ...:
//...
}
if (extensionAudioObjectType != 5 && bits_to_decode() >= 16) {
//...
}
// ...
GetAudioObjectType() {
audioObjectType; // 5 uimsbf
if (audioObjectType == 31) {
audioObjectType = 32 + audioObjectTypeExt; // 6 uimsbf
}
return audioObjectType;
}
下面是 ISO/IEC 14496-3, 1.5.1.1 Audio object type definition:
| ID | Type |
|---|---|
| 0 | Null |
| 1 | AAC main |
| 2 | AAC LC |
| 3 | AAC SSR |
| 4 | AAC LTP |
| 5 | SSR |
| … | … |
下面是 ISO/IEC 14496-3, 1.6.3.4 samplingFrequencyIndex:
| index | value |
|---|---|
| 0x0 | 96000 |
| 0x1 | 88200 |
| 0x2 | 64000 |
| 0x3 | 48000 |
| 0x4 | 44100 |
| 0x5 | 32000 |
| 0x6 | 24000 |
| 0x7 | 22050 |
| 0x8 | 16000 |
| 0x9 | 12000 |
| 0xa | 11025 |
| 0xb | 8000 |
| 0xc | 7350 |
| 0xd | reserved |
| 0xe | reserved |
| 0xf | escape value |
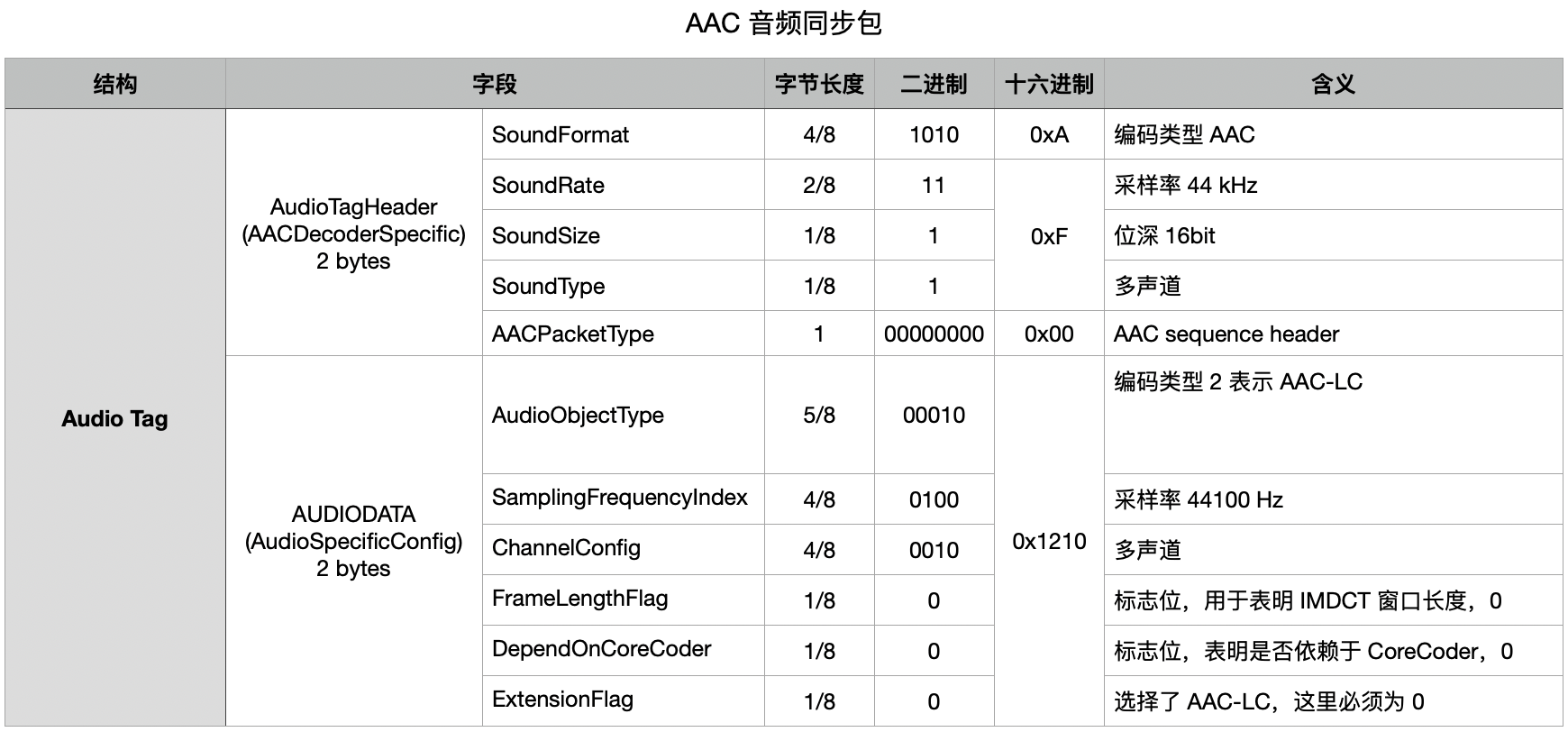
我们常用的 AAC 音频同步包的大小固定为 4 字节,前两个字节被称为 AACDecoderSpecificInfo,用于描述这个音频包应当如何被解析,后两个字节称为 AudioSpecificConfig,更加详细的指定了音频格式。下图是一个 AAC 音频同步包的示例:
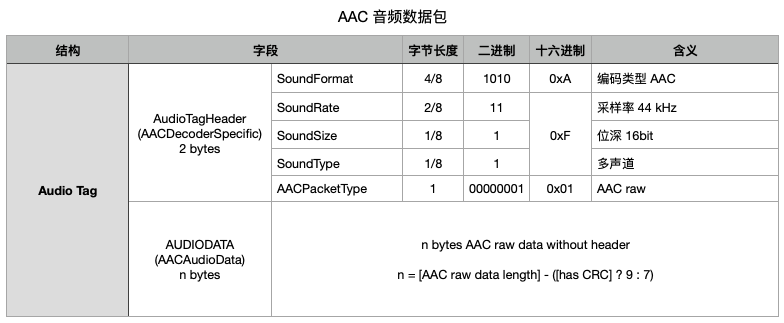
在完成 AAC 音频同步包的发送后,我们就可以向服务器推送普通的 AAC 数据包了。在发送数据包时,AACDecoderSpecificInfo 则变为 0xAF01,向服务器说明这个包是普通 AAC 数据包。如果这里的 AAC 数据有包含 7 个字节 ADTS 头(若存在 CRC 校验,则是 9 个字节),那么要去掉这个头后,把裸数据放到这里。如果这里是采集到的裸数据,没有 ADTS 头,那么这里就不需要这样处理了。下图是一个 AAC 音频数据包的示例:
对应的,在解析 FLV 时,如果封装的是 AAC 的音频,要在每帧 AAC ES 流前把 7 个字节 ADTS 头添加回来,这是因为 ADTS 是解码器通用的格式,纯的 AAC ES 流要打包成 ADTS 格式的 AAC 文件,解码器才能正常解码。在打包 ADTS 的时候,需要用到 samplingFrequencyIndex 这个信息,samplingFrequencyIndex 最准确的信息是存储在 AudioSpecificConfig 中。
有关 AudioSpecificConfig 结构解析的代码,可以参考 ffmpeg/libavcodec/mpeg4audio.c 中的 avpriv_mpeg4audio_get_config 函数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
int avpriv_mpeg4audio_get_config(MPEG4AudioConfig *c, const uint8_t *buf, int bit_size, int sync_extension)
{
GetBitContext gb;
int ret;
if (bit_size <= 0)
return AVERROR_INVALIDDATA;
ret = init_get_bits(&gb, buf, bit_size);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
return ff_mpeg4audio_get_config_gb(c, &gb, sync_extension);
}
int ff_mpeg4audio_get_config_gb(MPEG4AudioConfig *c, GetBitContext *gb, int sync_extension)
{
int specific_config_bitindex, ret;
int start_bit_index = get_bits_count(gb);
c->object_type = get_object_type(gb);
c->sample_rate = get_sample_rate(gb, &c->sampling_index);
c->chan_config = get_bits(gb, 4);
if (c->chan_config < FF_ARRAY_ELEMS(ff_mpeg4audio_channels))
c->channels = ff_mpeg4audio_channels[c->chan_config];
c->sbr = -1;
c->ps = -1;
if (c->object_type == AOT_SBR || (c->object_type == AOT_PS &&
// check for W6132 Annex YYYY draft MP3onMP4
!(show_bits(gb, 3) & 0x03 && !(show_bits(gb, 9) & 0x3F)))) {
if (c->object_type == AOT_PS)
c->ps = 1;
c->ext_object_type = AOT_SBR;
c->sbr = 1;
c->ext_sample_rate = get_sample_rate(gb, &c->ext_sampling_index);
c->object_type = get_object_type(gb);
if (c->object_type == AOT_ER_BSAC)
c->ext_chan_config = get_bits(gb, 4);
} else {
c->ext_object_type = AOT_NULL;
c->ext_sample_rate = 0;
}
specific_config_bitindex = get_bits_count(gb);
if (c->object_type == AOT_ALS) {
skip_bits(gb, 5);
if (show_bits_long(gb, 24) != MKBETAG('\0','A','L','S'))
skip_bits_long(gb, 24);
specific_config_bitindex = get_bits_count(gb);
ret = parse_config_ALS(gb, c);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
}
if (c->ext_object_type != AOT_SBR && sync_extension) {
while (get_bits_left(gb) > 15) {
if (show_bits(gb, 11) == 0x2b7) { // sync extension
get_bits(gb, 11);
c->ext_object_type = get_object_type(gb);
if (c->ext_object_type == AOT_SBR && (c->sbr = get_bits1(gb)) == 1) {
c->ext_sample_rate = get_sample_rate(gb, &c->ext_sampling_index);
if (c->ext_sample_rate == c->sample_rate)
c->sbr = -1;
}
if (get_bits_left(gb) > 11 && get_bits(gb, 11) == 0x548)
c->ps = get_bits1(gb);
break;
} else
get_bits1(gb); // skip 1 bit
}
}
//PS requires SBR
if (!c->sbr)
c->ps = 0;
//Limit implicit PS to the HE-AACv2 Profile
if ((c->ps == -1 && c->object_type != AOT_AAC_LC) || c->channels & ~0x01)
c->ps = 0;
return specific_config_bitindex - start_bit_index;
}
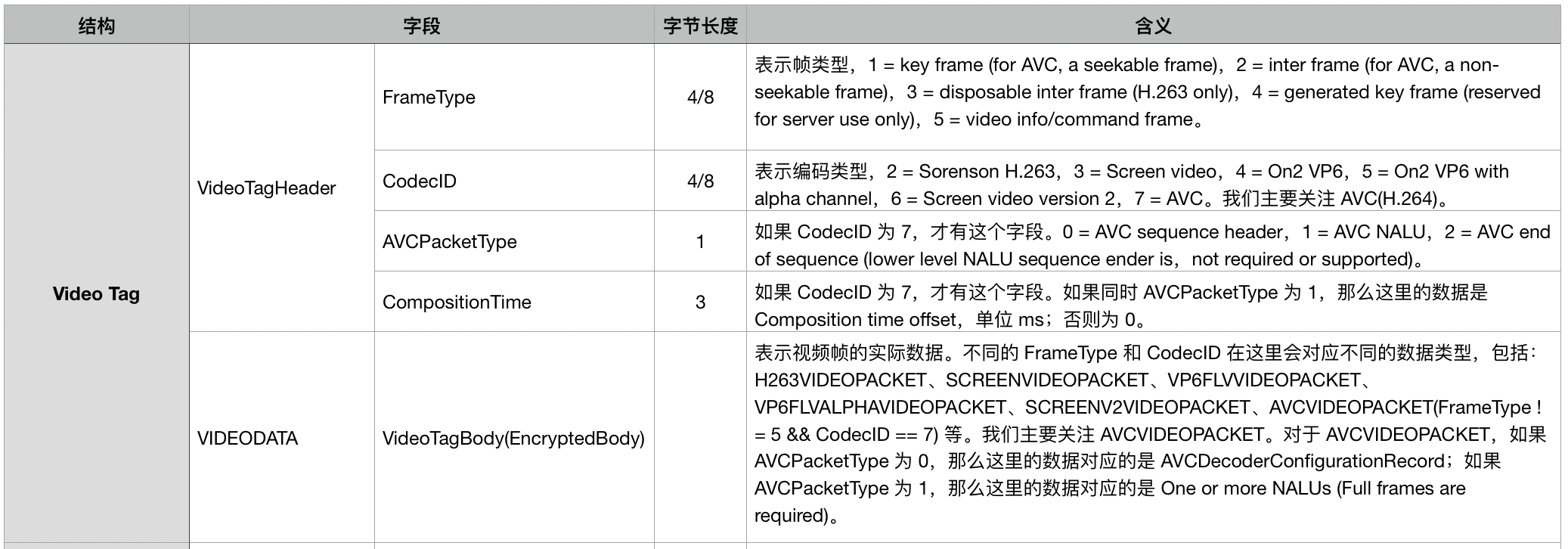
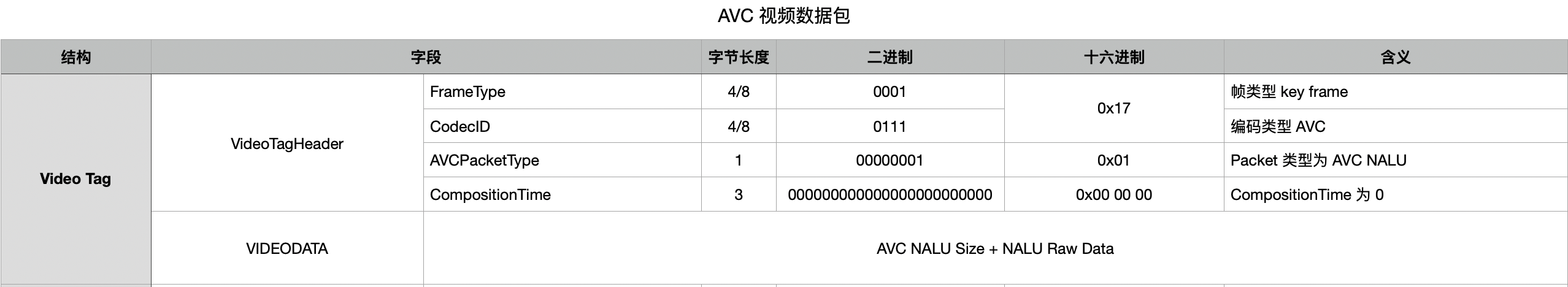
3、Video Tags 解析
Video Tag 的结构大致如下所示:
如上图所示,一般在 VideoTagHeader 后面跟着的就是 VIDEODATA 数据了,但是对于 AVC(H.264) 的编码格式来说,VideoTagHeader 会多出两个字段 AVCPacketType 和 CompositionTime。AVCPacketType 是表示后面 VIDEODATA 的类型,CompositionTime 则表示 pts 和 dts 的差值。
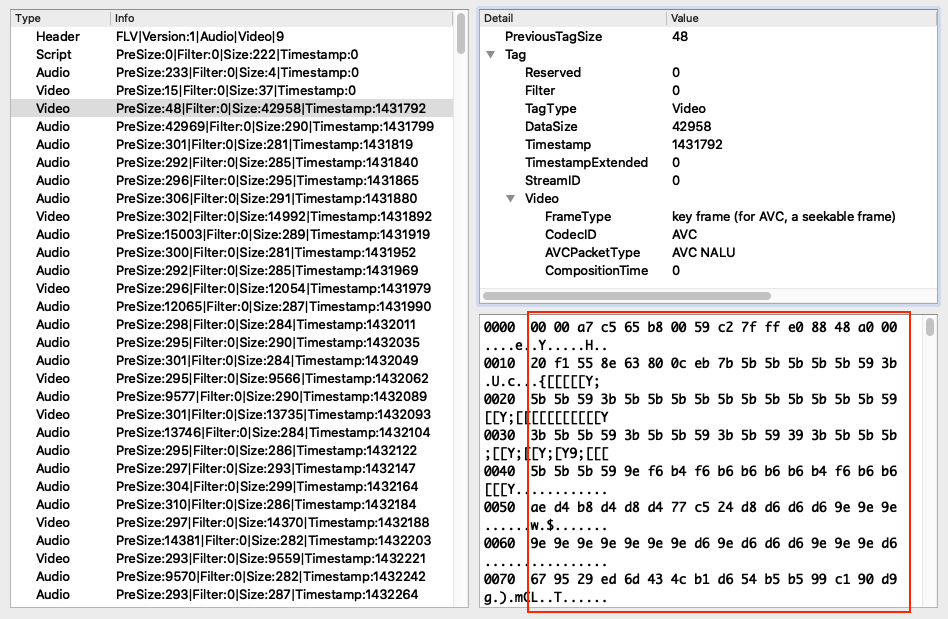
如果 AVCPacketType 为 0,那么这里的数据对应的是 AVCDecoderConfigurationRecord;如果 AVCPacketType 为 1,那么这里的数据对应的是 One or more NALUs(Full frames are required)。
AVCDecoderConfigurationRecord 记录的是 AVC(H.264)解码相关比较重要的 sps 和 pps 信息,解码器在解码数据之前需要首先获取的 sps 和 pps 的信息。在做 seek 或者断流重连等操作引起解码器重启时,也需要给解码器再传一遍 sps 和 pps 信息。
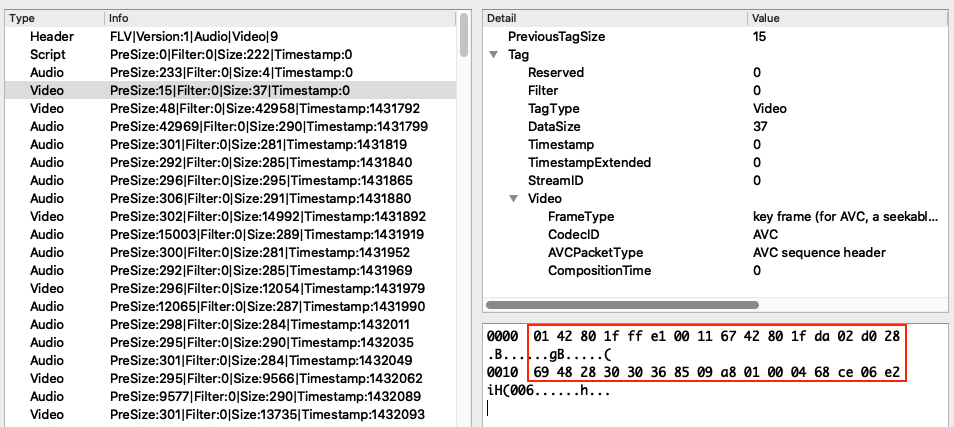
在 FLV 的文件中,一般情况下 AVCDecoderConfigurationRecord 只会出现一次,即第一个 Video Tag。如果视频使用 AVC,那么这个 Tag 就是 AVC sequence header,即 AVC 视频同步包。AVCDecoderConfigurationRecord 结构的在 ISO/IEC-14496-15 AVC file format 标准中有做说明。
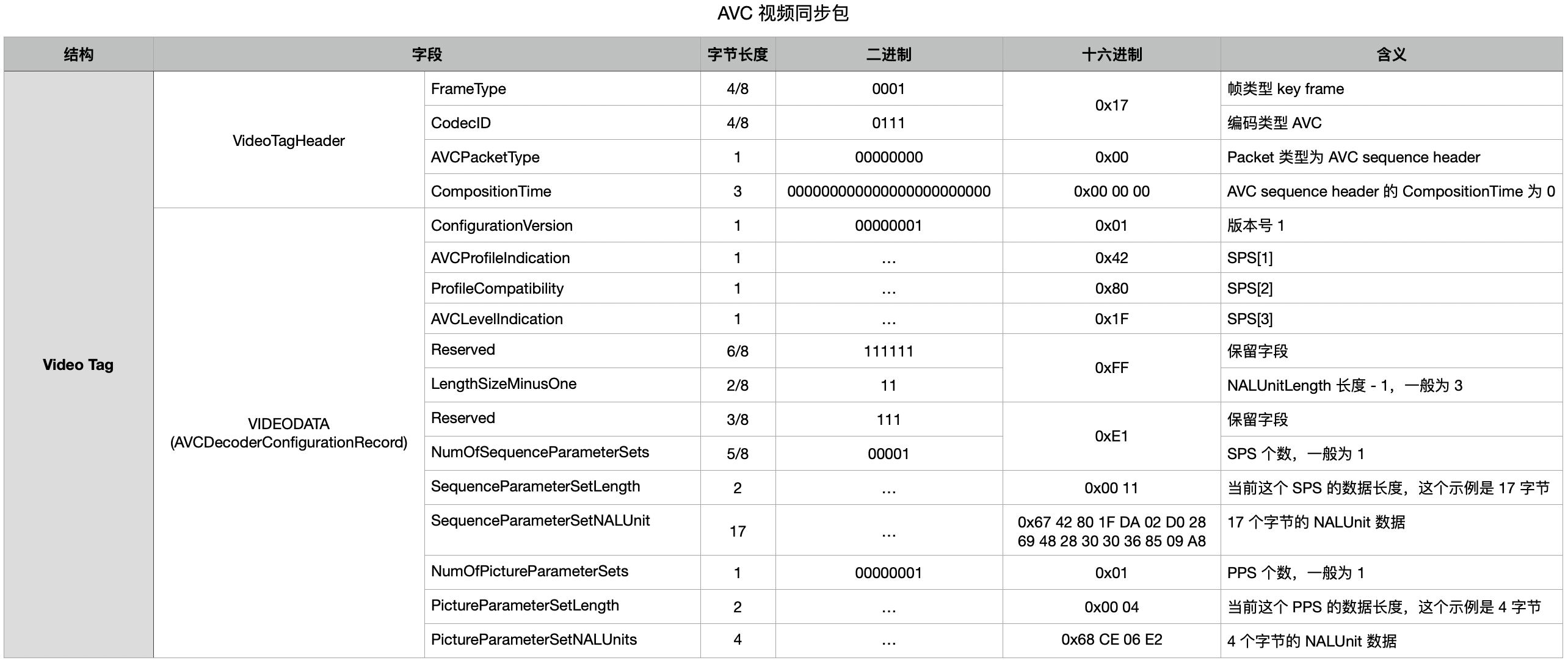
下面是 ISO/IEC 14496-15, 5.3.3.1.2 AVCDecoderConfigurationRecord:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
aligned(8) class AVCDecoderConfigurationRecord {
unsigned int(8) configurationVersion = 1;
unsigned int(8) AVCProfileIndication;
unsigned int(8) profile_compatibility;
unsigned int(8) AVCLevelIndication;
bit(6) reserved = '111111'b;
unsigned int(2) lengthSizeMinusOne;
bit(3) reserved = '111'b;
unsigned int(5) numOfSequenceParameterSets;
for (i = 0; i < numOfSequenceParameterSets; i++) {
unsigned int(16) sequenceParameterSetLength ;
bit(8*sequenceParameterSetLength) sequenceParameterSetNALUnit;
}
unsigned int(8) numOfPictureParameterSets;
for (i = 0; i < numOfPictureParameterSets; i++) {
unsigned int(16) pictureParameterSetLength;
bit(8*pictureParameterSetLength) pictureParameterSetNALUnit;
}
if (profile_idc == 100 || profile_idc == 110 ||
profile_idc == 122 || profile_idc == 144)
{
bit(6) reserved = '111111'b;
unsigned int(2) chroma_format;
bit(5) reserved = '11111'b;
unsigned int(3) bit_depth_luma_minus8;
bit(5) reserved = '11111'b;
unsigned int(3) bit_depth_chroma_minus8;
unsigned int(8) numOfSequenceParameterSetExt;
for (i = 0; i < numOfSequenceParameterSetExt; i++) {
unsigned int(16) sequenceParameterSetExtLength;
bit(8*sequenceParameterSetExtLength) sequenceParameterSetExtNALUnit;
}
}
}
下面是 ITU-T H.264(ISO/IEC 14496-10), A.2 Profiles:
| idc | Profile |
|---|---|
| 66 | Baseline |
| 77 | Main |
| 88 | Extended |
| 100 | High |
| 110 | High 10 |
| 122 | High 4:2:2 |
| 144 | (High 4:4:4; removed) |
| 244 | High 4:4:4 Predictive |
下面是 ITU-T H.264(ISO/IEC 14496-10), A.3 Levels:
1
2
3
Defined level_idc: 10, 9[^1], 11, 12, 13, 20, 21, 22, 30, 31, 32, 40, 41, 42, 50, 51, 52
[^1]: "level_idc==9" represents "Leve 1b" unless Baseline(Constrained Baseline), Main, or Extended profiles.
下面是 ISO/IEC 14496-15, 8.3.3.1.2 HEVCDecoderConfigurationRecord:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
aligned(8) class HEVCDecoderConfigurationRecord {
unsigned int(8) configurationVersion = 1;
unsigned int(2) general_profile_space;
unsigned int(1) general_tier_flag;
unsigned int(5) general_profile_idc;
unsigned int(32) general_profile_compatibility_flags;
unsigned int(48) general_constraint_indicator_flags;
unsigned int(8) general_level_idc;
bit(4) reserved = ‘1111’b;
unsigned int(12) min_spatial_segmentation_idc;
bit(6) reserved = ‘111111’b;
unsigned int(2) parallelismType;
bit(6) reserved = ‘111111’b;
unsigned int(2) chromaFormat;
bit(5) reserved = ‘11111’b;
unsigned int(3) bitDepthLumaMinus8;
bit(5) reserved = ‘11111’b;
unsigned int(3) bitDepthChromaMinus8;
bit(16) avgFrameRate;
bit(2) constantFrameRate;
bit(3) numTemporalLayers;
bit(1) temporalIdNested;
unsigned int(2) lengthSizeMinusOne;
unsigned int(8) numOfArrays;
for (j=0; j < numOfArrays; j++) {
bit(1) array_completeness;
unsigned int(1) reserved = 0;
unsigned int(6) NAL_unit_type;
unsigned int(16) numNalus;
for (i=0; i< numNalus; i++) {
unsigned int(16) nalUnitLength;
bit(8*nalUnitLength) nalUnit;
}
}
}
下面是 ITU-T H.265(ISO/IEC 23008-2), A.3 Profiles:
| idc | Profile |
|---|---|
| 1 | Main |
| 2 | Main 10 |
| 3 | Main Still Picture |
下面是 ITU-T H.265(ISO/IEC 23008-2), A.4 Tiers and levels:
| flag | Tier |
|---|---|
| 0 | Main |
| 1 | High |
| idc | Level |
|---|---|
| 30 | 1 |
| 60 | 2 |
| 63 | 2.1 |
| 90 | 3 |
| 93 | 3.1 |
| 120 | 4 |
| 123 | 4.1 |
| 150 | 5 |
| 153 | 5.1 |
| 156 | 5.2 |
| 180 | 6 |
| 183 | 6.1 |
| 186 | 6.2 |
下图是一个 AVC 视频同步包的示例,其中红框部分对应的是 VIDEODATA:
下图是一个 AVC 视频数据包的示例,其中红框部分对应的是 VIDEODATA:
有关 AVCDecoderConfigurationRecord 结构解析的代码,可以参考 ffmpeg/libavformat/avc.c 中的 ff_isom_write_avcc 函数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
int ff_isom_write_avcc(AVIOContext *pb, const uint8_t *data, int len)
{
if (len > 6) {
/* check for H.264 start code */
if (AV_RB32(data) == 0x00000001 ||
AV_RB24(data) == 0x000001) {
uint8_t *buf=NULL, *end, *start;
uint32_t sps_size=0, pps_size=0;
uint8_t *sps=0, *pps=0;
int ret = ff_avc_parse_nal_units_buf(data, &buf, &len);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
start = buf;
end = buf + len;
/* look for sps and pps */
while (end - buf > 4) {
uint32_t size;
uint8_t nal_type;
size = FFMIN(AV_RB32(buf), end - buf - 4);
buf += 4;
nal_type = buf[0] & 0x1f;
if (nal_type == 7) { /* SPS */
sps = buf;
sps_size = size;
} else if (nal_type == 8) { /* PPS */
pps = buf;
pps_size = size;
}
buf += size;
}
if (!sps || !pps || sps_size < 4 || sps_size > UINT16_MAX || pps_size > UINT16_MAX)
return AVERROR_INVALIDDATA;
avio_w8(pb, 1); /* version */
avio_w8(pb, sps[1]); /* profile */
avio_w8(pb, sps[2]); /* profile compat */
avio_w8(pb, sps[3]); /* level */
avio_w8(pb, 0xff); /* 6 bits reserved (111111) + 2 bits nal size length - 1 (11) */
avio_w8(pb, 0xe1); /* 3 bits reserved (111) + 5 bits number of sps (00001) */
avio_wb16(pb, sps_size);
avio_write(pb, sps, sps_size);
avio_w8(pb, 1); /* number of pps */
avio_wb16(pb, pps_size);
avio_write(pb, pps, pps_size);
av_free(start);
} else {
avio_write(pb, data, len);
}
}
return 0;
}
4、Data Tags 解析
Data Tag 的结构大致如下所示:
其中 ScriptTagBody 中的 Name 和 Value 字段都是 SCRIPTDATAVALUE 类型。Name 最终对应的是 String 类型,Value 最终对应的是 ECMA array 类型。
SCRIPTDATAVALUE 包含两个字段:Type 和 ScriptDataValue,前者表示数据的类型,后者装载实际数据。
- SCRIPTDATAVALUE:
- Type:定义数据的类型
- 0 = Number
- 1 = Boolean
- 2 = String
- 3 = Object
- 4 = MovieClip (reserved, not supported)
- 5 = Null
- 6 = Undefined
- 7 = Reference
- 8 = ECMA array
- 9 = Object end marker
- 10 = Strict array
- 11 = Date
- 12 = Long string
- ScriptDataValue:数据值
- Type:定义数据的类型
这些数据都是以 AMF(Action Message Format) 的形式编码。
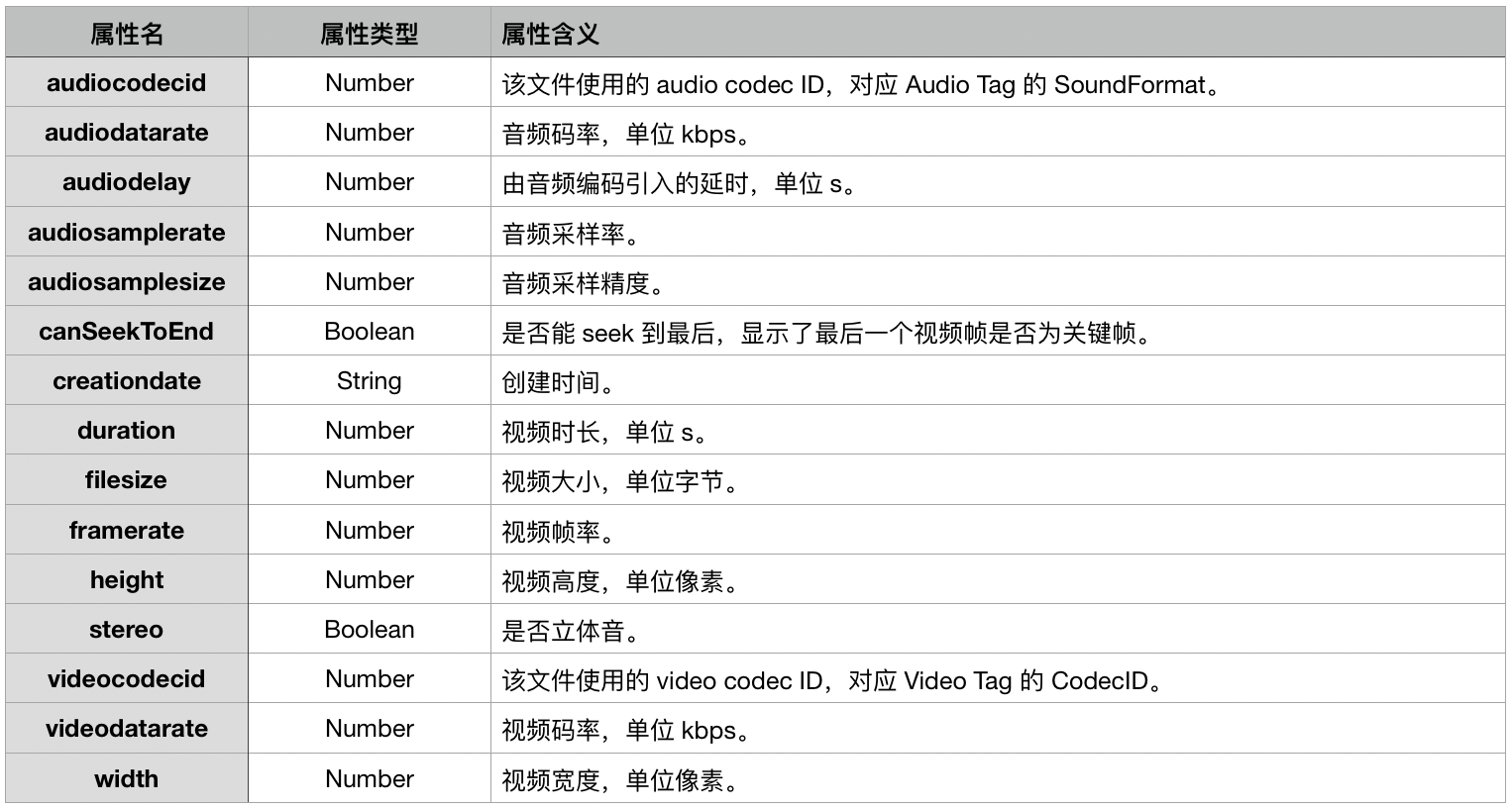
Data Tag 里可以承载不同的数据,其中我们最关心是的音视频的 metadata 元信息数据,这些信息是以一个 Name 为 onMetadata 的 SCRIPTDATA Tag 来存储的。
4.1、onMetadata 解析
onMetadata 包含着不同的属性,这些属性对于不同的 FLV 文件可能各不相同。
5、问题集锦
1、AAC 音频同步包字节不对导致微信小程序播放直播没声音?
遇到的问题是 AAC 音频同步包在推流端被丢了,腾讯云默认给补上了音频同步包的前 2 个字节,也就是 AACDecoderSpecificInfo,但是没有补上 AudioSpecificConfig。在微信小程序播放器中,不兼容这样的 AAC sequence header 所以就播不出声音了。
小结
通过上文的介绍,我们了解了 FLV 视频封装格式,并探讨了其中 Audio Tags、Video Tags、Data Tags 等模块的具体结构。
本文参考
- Adobe Flash Video File Format Specification
- 基于 libRTMP 的流媒体直播之 AAC、H264 推送
- RTMP 协议发送 H.264 编码及 AAC 编码的音视频
- ISO IEC 14496-15-2017
本文转自微信公众号
关键帧Keyframe,推荐您关注来获取音视频、AI 领域的最新技术和产品信息:你还可以加入我们的微信群和更多同行朋友来交流和讨论: